5 Pillars To Meaningful Intercultural Communication
There is an increasing focus in modern business on being global, diverse, and cosmopolitan. But why? Whilst you may think of these as little more than fun buzz words, understanding globality and diversity is crucial in today’s international environment – corporate or otherwise. Because this is the reality and future of the world… Read more »

Future-Proofing Employee-Employer Relationships
As we traverse the evolving landscape of employee-employer dynamics, it becomes evident that traditional paradigms are undergoing profound transformations. The contours of the modern workplace are shaped by nuanced expectations and interwoven complexities, demanding a human-centric approach to foster harmonious relationships and sustainable growth. In this article, we will delve into the various facets of… Read more »

8 Things You Should Know About Spain’s Business Culture
Embarking on a professional journey in Spain involves more than just mastering the language and loving the weather and the beautiful beaches; it requires a nuanced understanding of the country’s unique business culture and practices. Spain has become a hub for tech companies and young talent, but it is important to know how business is… Read more »

Unleashing the Power of Digital Change for Your Business
Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies into various aspects of a business, resulting in fundamental changes to how the organisation operates, delivers value to customers, and engages with stakeholders. It involves leveraging digital tools, technologies, and data to enhance business processes, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities for growth and innovation. The… Read more »

Lunar New Year 2024: What to Expect This Chinese New Year
Sunday, 10th February 2024 marks the beginning of the new lunar year. This year will be the Year of the Dragon, the fifth of all zodiac animals. This period stands out for its rarity and significance, emphasising the pursuit of dreams, creativity, and the expansion of horizons. It invites a year of generosity, compassion, and… Read more »

7 Things to Consider When Relocating an Employee to France
France is not only the country of baguette, good cheese, and excellent wine. It is much more complex and offers its challenges when in day-to-day living. Below are some tips to ensure that your employees settle well when relocating to this country: Improve your employee experience. A change in professional life leading to a change… Read more »

Unlocking Success: The Power of Talent Mapping in Competitive Markets
In the dynamic landscape of today’s talent market, staying ahead requires strategic insights and a proactive approach. One invaluable tool that organisations are leveraging to gain a competitive edge is talent benchmarking or market mapping. What is Talent Mapping? Talent benchmarking involves a comprehensive analysis covering salary ranges, benefits, qualifications, experience, and job responsibilities of… Read more »

How to Leverage Your Employer Branding for Talent Acquisition
In today’s competitive job market, it’s not enough to simply offer a competitive salary and benefits package to attract top talent. Companies must also have a strong brand culture that resonates with potential employees. But what exactly is brand culture, and how can you leverage it for talent acquisition? In this article, we’ll explore the… Read more »

Keep up to Date with 2024 Public Holidays in Australia
In Australia, there are 8 national public holidays observed as part of the National Employment Standards (NES) that underpin employment throughout the country. In addition to these key dates, some states and territories also have additional regional public holidays or substitute public holidays. Substitute public holidays mean that if a public holiday falls on… Read more »

Polyglot Bronze Winner in the HRD’s Service Provider Awards for Recruitment Firms
Polyglot, your trusted boutique recruitment consultancy, is thrilled to share the exciting news of securing the bronze medal in the recruitment firms category at the esteemed Human Resources Director’s sixth annual Service Provider Awards. This prestigious accolade is not just a recognition of our commitment to excellence but a celebration of our shared success in… Read more »

Australia
The abundant, ever-growing
island nation
Interested in doing business in Australia?
Here’s what you need to know about the
business climate, laws and regulations,
culture, and customs ‘down under’.

Country Snapshot

Official Language
Australian English

Currency
Australian Dollar (AUD)

Economy
13th in the world

World Zone
Asia Pacific / Oceania

Capital
Canberra
-
Key Facts & Figures
Location
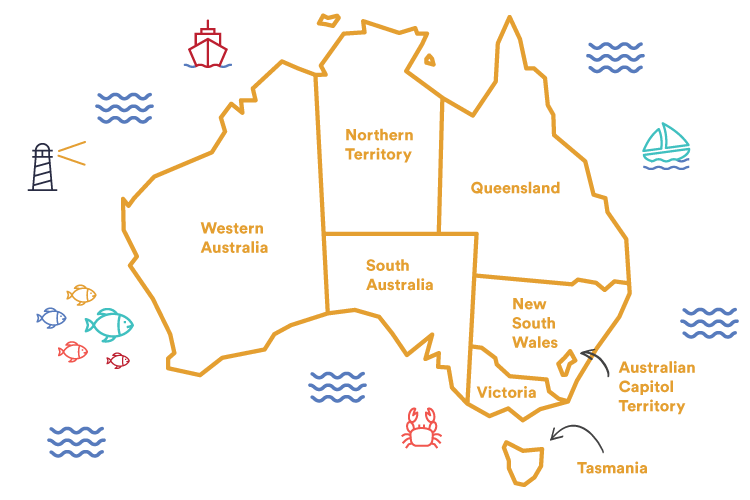
Located in the southern hemisphere, the Commonwealth of Australia is the sixth largest country by total land mass. This includes the mainland continent, the island state of Tasmania, and over 8,000 other islands located within its maritime borders.
Mainland Australia is also the world’s largest island and the smallest continent and is divided into six states and two territories: New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia, the Northern Territory, the Australian Capitol Territory and Tasmania.
Population
Australia’s population is approximately 26 million people. This continues to increase, with roughly one new immigrant arriving every 2 minutes and 20 seconds.
Australia ranks as the 2nd wealthiest nation in terms of wealth per adult, with its national GDP valued at A$1.69 trillion – roughly A$79.3k per capita (2019).
-
Economy
As a highly developed country, as well as being the world’s 13th largest economy, it comes as no surprise that Australia is a natural choice for many companies seeking to expand in the global marketplace.
With 28 consecutive years of annual economic growth, the rate of annual GDP growth is increasing exponentially, jumping from 2.1 per cent (2016-17) to 2.9 per cent (2017-18).
Australia’s GDP growth is projected to be 6.6% larger by the end of 2022 compared to pre-COVID 2019.
Furthermore, over the next five years (until 2023), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) predicts that Australia will outperform every other major advanced economy in the world.
Trade
With a strong financial system, low unemployment (3.9%), low public debt and a highly-skilled workforce, the Australian economy is driven by exports, with a strong focus on minerals, energy and agriculture.
Australia has strong trade and economic links with Asian-Pacific countries and is considered a gateway for American, European & Asian companies looking to explore trade in the region.
Top Imports & Exports
With strong trade ties to Asia, Europe, and the US, Australia enjoys a wide variety of export markets. The export value in 2020 was $299 billion, while imports came in at $241 billion.
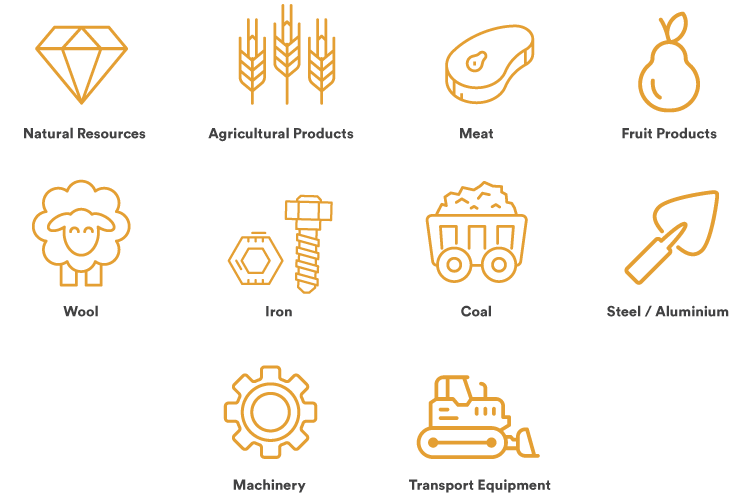
The country holds an abundance of natural resources, agricultural products (especially meat, wheat, and wool), as well as machinery and transport equipment – all of which make up its primary exports.
In 2009, China surpassed Japan to become Australia’s largest export market in Asia, with total merchandise exports now valued at A$47 billion. The primary export products to Asia include iron ore, coal, and LNG, followed by wool.
Top Australian merchandise exports to Europe include gold, coal, and food products such as oil-rich seeds and fruits. Major export products to the US include steel and aluminium.
Top imports into Australia include mineral fuels including oil, vehicles (such as cars, trucks, ships, etc.), electrical machinery and equipment (such as computers) as well as pharmaceuticals. Top import origins are China, the US, South Korea, Japan, and Thailand.

Free Trade Agreements
As a leading trade hub in the APAC region, Australia has FTAs with the U.S., Thailand, Chile, Singapore, China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Hong Kong, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Currently, India has an interim free trade agreement, as of 2 April, 2022. Still to be negotiated is one bilateral agreement with Indonesia, as well as four plurilateral agreements with the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), the Pacific Trade and Economic Agreement (PACER Plus) the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (RCEP), and the Trade in Services Agreement (TiSA) with the European Union.
It may be beneficial to know that US companies with Australian subsidiaries can trade with these countries with reduced or no tariffs in specified industries.
-
Legislation
Expanding to Australia? Here is a breakdown of the key things to keep in mind.
Company Setup
The Australian market boasts huge potential for business opportunities. Setting up your business in Australia can be done through various methods, such as partnering with an Employer of Record, registering as a foreign entity, or opening a local subsidiary or branch.
In order to simplify setup and best understand Australia’s legislative frameworks around company registration, click here.
Employment
Australia uses a standard employment contract template with a few modifications pertaining to probationary periods, employee benefits and PTO. Employment-at-will is not legal in Australia, and non-competition clauses are enforceable only if deemed reasonable by local authorities.
In Australia, Modern Awards are also key for understanding different industry and position categories, as they enforce minimum wage standards and working conditions.
Immigration
The TSS (subclass 482 – formerly 457) visa is most commonly used to employ skilled foreign workers in Australia. The visa can be sponsored by an Australian company with trading history (i.e. with a Standard Business Sponsorship, or SBS) or by a foreign company (i.e. with an Overseas Business Sponsorship, or OBS).
The visa candidate must, however, hold one of the approved occupations on the short-term (STSOL) or medium- to long-term (MLTSSL) list. Note that restrictions around visas in Australia, including these lists, change frequently.
Payroll
Payroll tax is levied by each state in Australia. Employees who work in different states in the same tax year may risk payroll tax and registration liability if they do not comply accordingly. As payroll registration is by the state where employees work, supplemental registration may be required when employees are hired and operate across state lines. In Australia, employers and employees follow a strict PAYG (Pay As You Go) system.
Tax
In Australia, the Financial Year ends on 30 June, while the Fringe Benefits Tax (FBT) Year ends on 31 March. Corporate tax returns have varying annual filing deadlines and can sometimes be as late as 30 June. The national sales tax is known as the Goods and Services Tax (GST) – the equivalent of the VAT in Europe. GST is a broad-based tax of 10% that applies to most goods, services, and other items sold or consumed within Australia. It is chargeable on any business connected to Australia, and the returns must be filed within four months from the end of the financial year.