Unsettled Employer-Employee Relationship
As we traverse the evolving landscape of employee-employer dynamics, it becomes evident that traditional paradigms are undergoing profound transformations. The contours of the modern workplace are shaped by nuanced expectations and interwoven complexities, demanding a human-centric approach to foster harmonious relationships and sustainable growth. In this article, we will delve into the various facets of… Read more »

8 Things You Should Know About Spain’s Business Culture
Embarking on a professional journey in Spain involves more than just mastering the language and loving the weather and the beautiful beaches; it requires a nuanced understanding of the country’s unique business culture and practices. Spain has become a hub for tech companies and young talent, but it is important to know how business is… Read more »

Unleashing the Power of Digital Change for Your Business
Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies into various aspects of a business, resulting in fundamental changes to how the organisation operates, delivers value to customers, and engages with stakeholders. It involves leveraging digital tools, technologies, and data to enhance business processes, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities for growth and innovation. The… Read more »

Lunar New Year 2024: What to Expect This Chinese New Year
Sunday, 10th February 2024 marks the beginning of the new lunar year. This year will be the Year of the Dragon, the fifth of all zodiac animals. This period stands out for its rarity and significance, emphasising the pursuit of dreams, creativity, and the expansion of horizons. It invites a year of generosity, compassion, and… Read more »

7 Things to Consider When Relocating an Employee to France
France is not only the country of baguette, good cheese, and excellent wine. It is much more complex and offers its challenges when in day-to-day living. Below are some tips to ensure that your employees settle well when relocating to this country: Improve your employee experience. A change in professional life leading to a change… Read more »

Unlocking Success: The Power of Talent Mapping in Competitive Markets
In the dynamic landscape of today’s talent market, staying ahead requires strategic insights and a proactive approach. One invaluable tool that organisations are leveraging to gain a competitive edge is talent benchmarking or market mapping. What is Talent Mapping? Talent benchmarking involves a comprehensive analysis covering salary ranges, benefits, qualifications, experience, and job responsibilities of… Read more »

How to Leverage Your Employer Branding for Talent Acquisition
In today’s competitive job market, it’s not enough to simply offer a competitive salary and benefits package to attract top talent. Companies must also have a strong brand culture that resonates with potential employees. But what exactly is brand culture, and how can you leverage it for talent acquisition? In this article, we’ll explore the… Read more »

Keep up to Date with 2024 Public Holidays in Australia
In Australia, there are 8 national public holidays observed as part of the National Employment Standards (NES) that underpin employment throughout the country. In addition to these key dates, some states and territories also have additional regional public holidays or substitute public holidays. Substitute public holidays mean that if a public holiday falls on… Read more »

Polyglot Bronze Winner in the HRD’s Service Provider Awards for Recruitment Firms
Polyglot, your trusted boutique recruitment consultancy, is thrilled to share the exciting news of securing the bronze medal in the recruitment firms category at the esteemed Human Resources Director’s sixth annual Service Provider Awards. This prestigious accolade is not just a recognition of our commitment to excellence but a celebration of our shared success in… Read more »

Keep up to Date with 2024 Public Holidays in France
France observes and celebrates many holidays throughout the year, whether religious holidays, seasonal holidays, or national holidays relevant to the history of France. Should your foreign business have a presence in France, or you’re interested in learning more about French culture it is important to keep on top of all public holidays from an HR… Read more »

Germany
The home of Europe’s
largest economy
Interested in doing business in Germany?
Here’s what you need to know about the
business climate, laws and regulations,
culture, and customs in Germany.

Country Snapshot

Official Language
German

Currency
Euro (EUR)

Economy
4th in the world

World zone
Europe

Capital
Berlin
-
Key Facts & Figures
Location
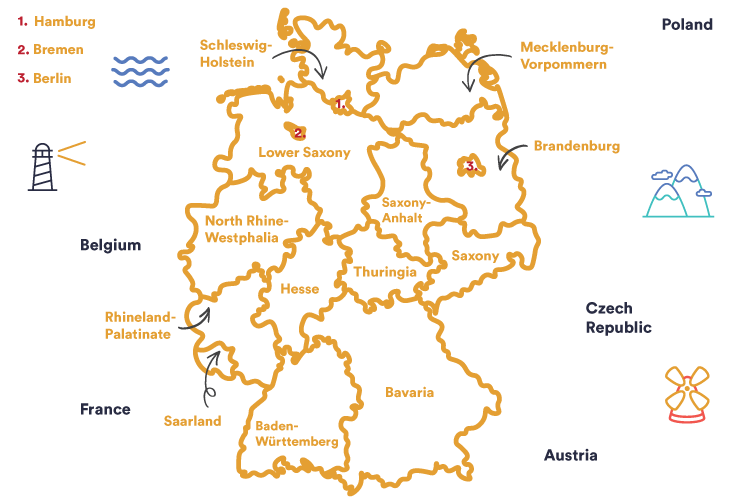
Located in the northern part of central Europe, Germany is officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany, Deutschland or Bundesrepublik Deutschland. It is one of Europe’s largest countries. It covers the area between the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxemburg, France, Switzerland, Austria, Czech Republic, Poland, Denmark, the Baltic Sea and the North Sea.
There are 16 German states, each with their own head of government, legislature and government party coalitions.
Population
The German population is roughly 79.9 million people. With a life expectancy of almost 82 years and a steady decline in the birth rate to 1.5 births per woman, the country is now spending close to $265 million every year in an attempt to reverse the declining population. The population growth rate is currently around the 0.2 per cent mark but is expected to dip into the negatives by 2025.
-
Economy
Germany is the largest economy in Europe and the 4th largest in the world with a GDP of approximately 4.238 trillion USD. Economic growth remains steady around 2% annually. Inflation has been slowly increasing to 2.0% from 0.4% in 2016.
Germany continues to experience large fiscal surpluses, which in turn has led to the steady decline of the public debt ratio.
Trade
With a strong financial system, low unemployment, low public debt and a highly-skilled workforce, the driving force of the German economy has shifted from exports to consumption and investment. Germany is the largest consumer market in Europe and much of its trade is focused on some of the world’s largest trade events, including MEDICA, the Hannover Fair, Automechanika and the ITB Tourism Show. For these reasons, many companies seek to base their European / international expansion in Germany.
Top Imports & Exports
With strong trade ties primarily with Europe, but also with Asia and the US. The export value in 2017 was $1.33 trillion, while imports came in at $1.08 trillion.
The country is primarily focused on exporting manufactured goods, with a focus on transportation for products such as cars, vehicle parts and planes, helicopters and/or spacecraft. Machinery and medical products also make up a large portion of German exports.
Germany’s largest trade partner, in terms of exporting its goods, is the United States, followed by France, China and the rest of the European Union. In terms of imports, China accounts for 10%, followed by much of the European Union and the United States.
Top imports into Germany include many of the same goods exported from the country, including machinery, transportation and chemical products.
Free Trade Agreements
As part of the European Union, Germany enjoys free trade with the rest of the European countries and is able to negotiate trade agreements with the backing of the EU. There are agreements with Vietnam, New Zealand, Australia, Singapore, Mexico, Japan, Canada and the Mercosur group in focus, but also many more currently in play.
-
Legislation
Expanding to Germany? Here is a breakdown of the key things to keep in mind.
Company Setup
There are many ways that a business can be set up in Germany. International companies might choose to register a branch office, open a subsidiary, or form a general / limited partnership.
Employment
Most of the population, over 60% of the German workforce, is employed by SMEs. The unemployment rate is currently around 5.3%, which has fallen by 1% over the last 3 years.
German employment laws tend to be more favourable towards the employee in terms of termination protection, applicable collective bargaining agreements, and holidays.
Grants are available to businesses looking to recruit and employ people unable to work due to personal circumstances, such as disability or long-term unemployment.
Immigration
From Germany, companies have access to the European talent pool. All EU citizens are able to work in Germany without a visa. Those recruited from outside of the EU are required to apply for and obtain a residence permit in order to work and live within Germany for more than 3 months. The visa is obtained from the German embassy consulate in the applicant’s country of permanent residence.
Payroll
Payroll in Germany requires companies to obtain an employer number and registrations from the country’s tax and social security authorities. Employment law encompasses the employees right to join a union, a minimum wage and legal entitlement to time off.
In terms of tax collection, it is the employer’s responsibility to calculate the amount of income tax for each employee. This amount should be withheld from gross payments each month and submitted to the appropriate tax office by the 10th of the following month.
Employers and employees must both contribute to social insurance, including health, pension, unemployment and nursing care.
Tax
In Germany, the financial year follows a standard calendar year, ending on 31 December. Corporation tax is 15.825% on company profits. Business can deduct expenses from computations of taxable income. The tax return must be filed electronically by 31 July of the following year. If working with a tax advisor, filing can be extended to the last day of February of the second year following the tax year.
VAT is applied on the sale of all goods and the provision of services at a rate of 19%, potentially reduced to 7% on certain transactions. A refund will be paid if the input tax exceeds the VAT.