5 Pillars To Meaningful Intercultural Communication
There is an increasing focus in modern business on being global, diverse, and cosmopolitan. But why? Whilst you may think of these as little more than fun buzz words, understanding globality and diversity is crucial in today’s international environment – corporate or otherwise. Because this is the reality and future of the world… Read more »

Future-Proofing Employee-Employer Relationships
As we traverse the evolving landscape of employee-employer dynamics, it becomes evident that traditional paradigms are undergoing profound transformations. The contours of the modern workplace are shaped by nuanced expectations and interwoven complexities, demanding a human-centric approach to foster harmonious relationships and sustainable growth. In this article, we will delve into the various facets of… Read more »

8 Things You Should Know About Spain’s Business Culture
Embarking on a professional journey in Spain involves more than just mastering the language and loving the weather and the beautiful beaches; it requires a nuanced understanding of the country’s unique business culture and practices. Spain has become a hub for tech companies and young talent, but it is important to know how business is… Read more »

Unleashing the Power of Digital Change for Your Business
Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies into various aspects of a business, resulting in fundamental changes to how the organisation operates, delivers value to customers, and engages with stakeholders. It involves leveraging digital tools, technologies, and data to enhance business processes, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities for growth and innovation. The… Read more »

Lunar New Year 2024: What to Expect This Chinese New Year
Sunday, 10th February 2024 marks the beginning of the new lunar year. This year will be the Year of the Dragon, the fifth of all zodiac animals. This period stands out for its rarity and significance, emphasising the pursuit of dreams, creativity, and the expansion of horizons. It invites a year of generosity, compassion, and… Read more »

7 Things to Consider When Relocating an Employee to France
France is not only the country of baguette, good cheese, and excellent wine. It is much more complex and offers its challenges when in day-to-day living. Below are some tips to ensure that your employees settle well when relocating to this country: Improve your employee experience. A change in professional life leading to a change… Read more »

Unlocking Success: The Power of Talent Mapping in Competitive Markets
In the dynamic landscape of today’s talent market, staying ahead requires strategic insights and a proactive approach. One invaluable tool that organisations are leveraging to gain a competitive edge is talent benchmarking or market mapping. What is Talent Mapping? Talent benchmarking involves a comprehensive analysis covering salary ranges, benefits, qualifications, experience, and job responsibilities of… Read more »

How to Leverage Your Employer Branding for Talent Acquisition
In today’s competitive job market, it’s not enough to simply offer a competitive salary and benefits package to attract top talent. Companies must also have a strong brand culture that resonates with potential employees. But what exactly is brand culture, and how can you leverage it for talent acquisition? In this article, we’ll explore the… Read more »

Keep up to Date with 2024 Public Holidays in Australia
In Australia, there are 8 national public holidays observed as part of the National Employment Standards (NES) that underpin employment throughout the country. In addition to these key dates, some states and territories also have additional regional public holidays or substitute public holidays. Substitute public holidays mean that if a public holiday falls on… Read more »

Polyglot Bronze Winner in the HRD’s Service Provider Awards for Recruitment Firms
Polyglot, your trusted boutique recruitment consultancy, is thrilled to share the exciting news of securing the bronze medal in the recruitment firms category at the esteemed Human Resources Director’s sixth annual Service Provider Awards. This prestigious accolade is not just a recognition of our commitment to excellence but a celebration of our shared success in… Read more »

Spain
The prolific peninsula for business and culture
Interested in doing business in Spain?
Here’s what you need to know about the
business climate, laws and regulations,
culture, and customs in Spain.

Country Snapshot

Official Language
Spanish

Currency
Euro

Economy
14th in the world

World Zone
Europe

Capital
Madrid
-
Key Facts & Figures
Location
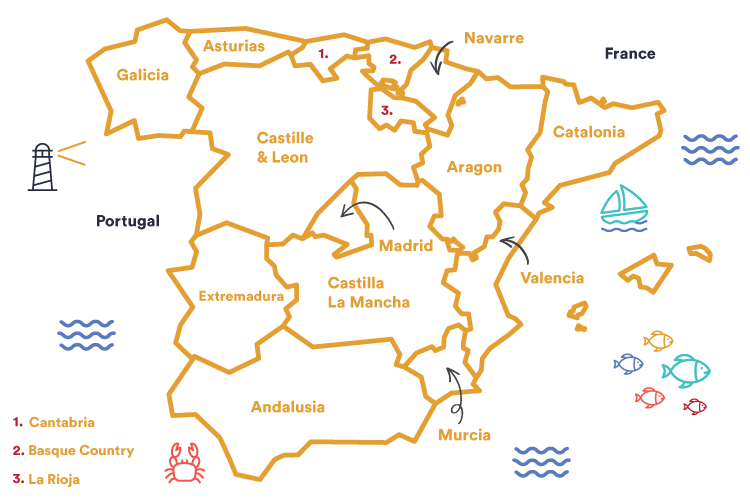
Spain is a country on Europe’s Iberian Peninsula, which includes 17 autonomous regions with diverse geography and cultures. Its territory also includes the Canary Islands off the coast of Africa and the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
Population
Spain’s population is approximately 47.3 million people.
Spain ranks as the 14th largest economy with its national GDP valued at $1.715 trillion. -
Culture
The business culture in Spain is generally characterised by a traditional and hierarchical structure, with clear divisions between management and workers. Relationship-building and integrity are highly valued in the Spanish business world, with the family unit serving as a central focus. The pace of business in Spain mirrors the energetic yet unhurried rhythm of daily life.
Public holidays play a significant role in shaping work schedules and fostering extended breaks for employees in Spain, contributing to the unique tapestry of Spanish business culture. These holidays, rooted in cultural and historical significance, often influence the pace and timing of business activities, highlighting the importance of considering the local calendar for effective planning and engagement in the Spanish professional landscape.
-
Economy
The economy of Spain is one of the largest in the world by purchasing power parity. The country is a member of the European Union, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and the World Trade Organisation.
Also, the Spanish economy is the fifth-largest in Europe behind Germany, United Kingdom, Italy, and France. It is the fourth-largest in the Eurozone, based on nominal GDP.
Trade
Spain is part of the harmonised trade system of the EU. As such, imports and exports are covered by the EU Taxation and Customs Union.
Top Imports & Exports
Spain’s most valuable exports are cars, followed by refined petroleum oils, automotive parts or accessories, drugs and medicines, trucks, and olive oil.
Spain’s number one import product is crude oil, followed by imported cars, auto parts and accessories, medication mixes in dosage, petroleum gases, and refined petroleum oils.
Free Trade Agreements
Spain has been a member of the WTO since 1 January 1995, and a member of GATT since 29 August 1963. It is a Member State of the European Union. All EU Member States are WTO members, as is the EU (until 30 November 2009 known officially in the WTO as the European Communities for legal reasons).
-
Legislation
Expanding to Spain? Here is a breakdown of the key things to keep in mind.
Company Setup
The Spanish market boasts huge potential for business opportunities. Setting up your business in Spain can be done through various methods, such as partnering with an Employer of Record or ETT (Empresa de Trabajo Temporal) to outsource employment, opening a representative office, setting up a branch, or establishing a subsidiary in Spain.
Curious to simplify setup and best understand Spain’s legislative frameworks around company registration? Click here for more information.
Payroll
In Spain, the personal income tax is called the IRPF. It works following a dual system and is levied both at the national and municipal level. Therefore, Spanish income tax rates are different from one region to another.
The deadline to submit tax assessments can vary. Generally, taxes must be filed by the 20th of each month or by the 20th of each month following the end of a quarter. Late penalties and other fees may apply.
Non-resident companies are eligible for a special Tax Regime by the Spanish Government. To comply with Spanish regulations, all companies must register at the Tax Office (Agencia Tributaria) to get a Tax Identification Code. To learn more, click here.
Employment
Employment in Spain is highly regulated and very protective of employee rights. Temporary contracts are the most common. Indefinite or permanent contracts are quite rare and difficult to obtain in the current economic climate. Both have minimum employment terms and conditions that employers must observe.
There are 3 types of workers; general employees, executives, and self-employed who have their separate regulation and jurisdiction.
The probation period is not compulsory in Spain, but it could be required, depending on companies’ policy.
However, in Spain, as jobs are grouped into categories, each category can have its own set of regulations. To learn more, download our eBook here.
Immigration
Everyone outside the EU/EEA states and Switzerland requires a work permit to work freely in Spain. The employer needs to request the work permit on the employee’s behalf; however, it might take up to 8 months to process. Once the work permit has been granted, the employee must apply for a residence Spanish visa.
After arriving in Spain, foreign workers must:
– Register in the corresponding Social Security scheme.
– Apply for a foreigner identity card (NIE).
For more information on this, continue reading here.
Tax
As with many European countries, the Tax Year runs on the calendar year, from the 1st of January to the 31st December.
The general rate of company tax is 25% and must be filed within 6 months and 25 days after the end of the accounting period.
Companies pay social security tax equal to 29.9% of the employee’s salary, up to a salary threshold of EUR 3,596.98. Moreover, employees are also liable to pay social security contributions.
The national sales tax on goods and services is known as the IVA, which is 21%.